A Transcription Unit Contains Which of the Following
A Elongation b Initiation c Phosphorylation d Peptide bond formation. These assemblies differ from those at the UCSC Genome Browser web site.

Bacterial Rna An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
We hope you find our assemblies useful.
. Use the labels to explain what mutations may have resulted in each mRNADrag the correct label to each location in the table. The stretch of DNA that is transcribed into an RNA molecule is called a transcription unit. B The small subunit of the ribosome binds to the 5.
A transcription unit codes the sequence that is translated into protein. Labels may be used once more than once or not at all. Elongation RNA is synthesized according to DNARNA base pairing.
Recent structural work showed that TEFM contains a pseudonuclease core that forms a sliding clamp around the mtDNA downstream of the transcribing POLRMT. RNA polymerase I is unusual in that it transcribes just a single set of genes. Tandem sites of transcription termination are located following the trpA structural gene.
The first is protein-factor-independent a so-called intrinsic terminator while the second required the protein Rho. Eukaryote ribosomes have a small 40S subunit which contains the 18S rRNA subunit and a large 60S subunit which contains the 5S 58S and 28S rRNA subunits. Transcription factors assemble at a specific promoter region along the DNA.
This is because the positive-sense strand contains the sequence information needed to translate the viral proteins needed for viral replication. This forms the basis of the polypeptide chain. During transcription enzymes called RNA polymerases build RNA molecules that are.
Mutation in a splicing signal sequence in the intron. Both Fos and Jun proteins the major components of the transcription factor activator protein-1 AP-1 bind to palindromic sequences in DNA known as TRE sites TGA C G TCA which mediate gene induction following phorbol ester treatment. It contains the reference sequence and working draft assemblies for many Drosophila genomes currently annotated by students participating in the GEP.
The capability of TEFM to abolish premature transcription termination has been proposed to function as the switch from replication to the transcription of the LSP-derived primary transcript. The UCSC Genome Browser is developed and maintained by the Genome Bioinformatics. Which of the following steps occurs last in the initiation phase of translation.
It also directs and regulates protein synthesis. Because it provides the template for ordering the sequence of nucleotides in an RNA transcript. Whilst Jun can bind to DNA as a homodimer Fos is unable to homodimerize and cannot bind to DNA without the formation of a FosJun.
Coli the small subunit is described as 30S which contains the 16S rRNA subunit and the large subunit is 50S which contains the 5S and 23S rRNA subunits for a total of 70S Svedberg units are not additive. During transcription the enzyme RNA polymerase green uses DNA as a template to produce a pre-mRNA transcript pink. This article contains phonetic symbols.
This leaves the A site free for further binding while the P site contains a tRNA molecule attached to an amino acid that is attached to another amino acid. Without proper rendering support you may see question marks boxes or other symbols instead of phonetic symbols. This process is catalyzed by a viral RNA replicase.
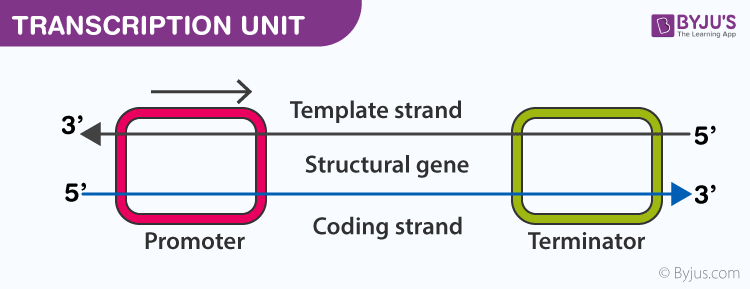
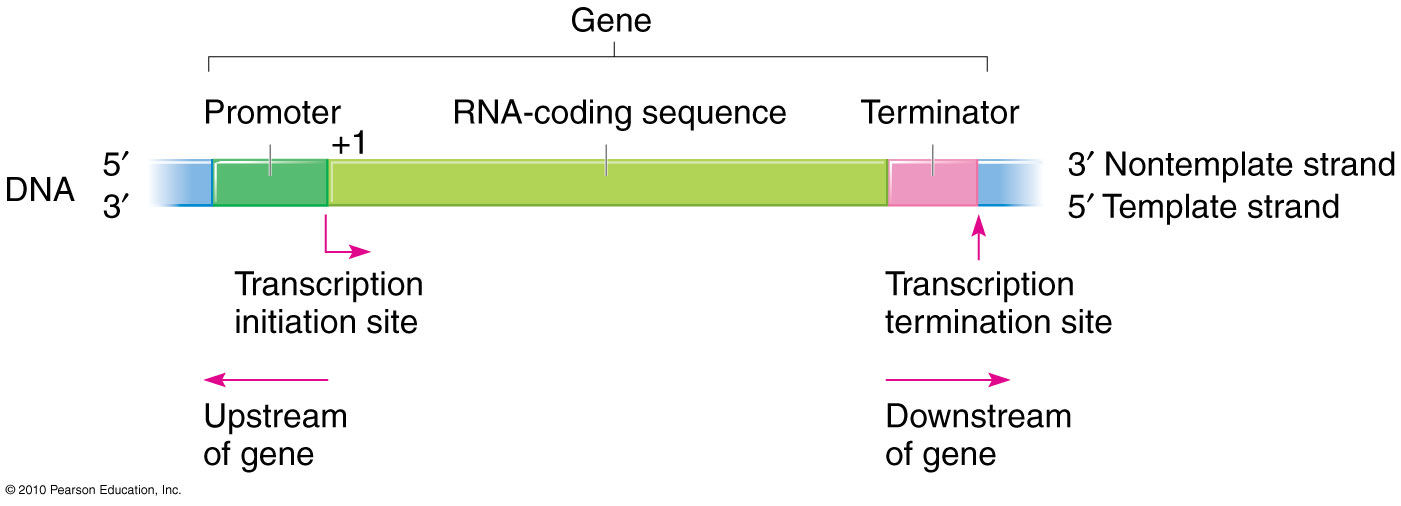
More than one gene may reside in a transcription unit. A DNA transcription unit encoding for a protein may contain both a. Inserting it with the help of other factors between the strands of the DNA double helix.
Transcription is the first step in decoding a cells genetic information. The term transcription unit refers to the segment of DNA between the sites of initiation and termination of transcription by RNA polymerase. The DNA strand which is used in RNA synthesis is called template strand.
These genes are expressed continuously in most cells but the rate of transcription varies during the cell cycle and is subject to a certain amount of tissue-specific regulation. It manoeuvres the RNA polymerase into place. The length of DNA following the promoter is a gene and it contains the recipe for a protein.
Which of the following molecules are produced during transcription. Transcription proceeds in the following general steps. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in.
The multiple copies of the transcription unit containing the 28S 58S and 18S rRNA sequences Section 321. Completion of transcription of the operon yields a polycistronic messenger RNA. A mediator protein complex arrives carrying the enzyme RNA polymerase.
The following description of this three-stage process applies generally to all cells but specific variations within the process may occur depending on organism and cell type. Another tRNA molecule then binds to the A site and peptidyl transferase catalyzes the creation of a peptide bond between this new amino acid and the amino acid. The International Phonetic Alphabet IPA is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script.
A A peptide bond is formed between two adjacent amino acids. Which of the following processes is an example of a post-translational modification. The following eukaryotic structural gene contains two introns and three exonsThe table below shows four possible mRNA products of this gene.
The pre-mRNA is processed to form a mature mRNA molecule that can be translated to build the protein molecule polypeptide encoded by the original gene. Ribosomes can initiate translation at any of the five major ribosome binding sites on this. The official chart of the IPA revised in 2020.

Dna Transcription Learn Science At Scitable

What Is Transcription Stages Of Transcription Rna Polymerase
Comments
Post a Comment